Anterior edema may be a physiological phenomenon or degenerative change related to patient age weight and knee movement or mechanics. Subcutaneous fat and fat in bone marrow.

A Sagittal Proton Density B Axial Fat Saturated T2 And C Coronal Download Scientific Diagram
An image produced by controlling the selection of scan parameters to minimize the effects of T1 and T2 resulting in an image dependent primarily on the density of protons in the imaging volume.

Proton density mri knee. A secondary goal was to compare the imaging appearance of knee abnormalities depicted with 5-minute DESS paired with a 2-minute coronal proton-density. The signal-to-noise ratio contrast-to-noise ratio CNR and anatomical. The PDW contrast provides data in which the ligaments menisci and cartilage can be simultaneously assessed for diagnosis with a reasonable scanning time.
We concur with the authors that proton densityweighted MR imaging sequences are well-suited for the visualization of hyaline cartilage. A slice through the knee from medial to lateral. Dedicated knee coil 8 channel 14 to 16 cm field of view 25 to 5 mm slice thickness Rarely use intravenous gadolinium Exam time 15 minutes MRI Pulse Sequences T1 weighted Sequences Fat sensitive Good anatomic resolution Proton Density Sequences Fat and fluid sensitive Best anatomic resolution.
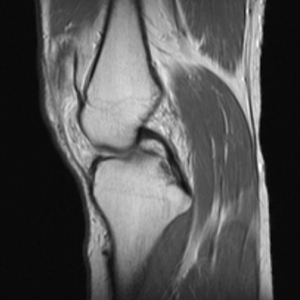
The Sagittal PD FSE sequence is designed to image the Anterior Cruciate Ligament ACL. Sagittal proton-density image of the knee shows a sprained posterior cruciate. When an MRI sequence is set to produce a PD-weighted image it is the tissues with the higher concentration or density of protons hydrogen atoms which produce the strongest signals and appear the brightest on the image.
Recently 3D imaging sequences appear to have a role for diagnosis. The orientation is a sagittal oblique along the orientation of the ACL. Proton density PD image characteristics.
Fast spin-echo proton density-weighted MR imaging sequences can be used to evaluate the cartilage of the knee with accuracy comparable to that of previously reported cartilage-specific sequences. Creating a lateral view as if scrolling through the knee from. We would like to comment on the advantages of additional fat suppression which increases the value of proton.
Historically the use of proton-density PD weighted sequences has been favored over T2-weighted sequences for detection of meniscal tears. It is postulated that the hydrogen nuclei within a tear are bound to macromolecules rather than being free which gives them a. Enhances tissues with high proton density fatty bone marrow hyaline cartilage muscles Planes.
The routine knee protocol need only consist of four sequences. The higher the number of protons in a given unit of tissue the greater the transverse component of. Proton density image.
There are two fundamental tenets of MSK imaging. 24 healthy volunteers who underwent MRI by both sagittal PD-weighted FSE and FRFSE sequences were evaluated. Proton density contrast is a quantitative summary of the number of protons per unit tissue.
This proton density-weighted coronal knee image shows a medial meniscus tear long arrow. Proton density weighted sequence produces contrast mainly by minimizing the impact of. Sagittal Proton density FSE.
The purpose of this study was to compare the proton-density PD-weighted fast spin-echo FSE and fast-recovery FSE FRFSE sequences for the evaluation of the anatomical structures of the knee. All other characteristics of the PD fat saturated images remain same as the PD image. Subcutaneous fat and fatty marrow are bright although not as bright as on a T1WI.
In MRI imaging we have many pulse sequences used for the evaluation of patellar cartilage one of the ideal pulse sequences is fat-suppressed proton density FS-PD which is very valuable in evaluating patellar cartilage as it has high spatial resolution suitable contrast-to-noise CNR ratio and good scan time 3 4. A slice through the knee from front to back. T1 post-intrarticular and post.
The easiest way to identify proton density PD fat saturated images is to look for adipose tissues in the body eg. Clinical knee MRI protocols require upwards of 15 minutes of scan time. This represents arthrofibrosis or a cyclops lesion which is causing impingment in extension of the knee.
Therefore basic MR protocols include anatomy defining sequences such as. Areas contain adipose tissues appear as dark on PD fat saturated images. T1 GREs and Proton Density PD or 1st echo T2 and fluid sensitive sequences such as Inversion Recovery IR and PD fat saturation although there is overlap between them.
Additionally internal structures of the knee joint such as synovium menisci ligaments and tendons can be excellently depicted with this technique 26. A proton density weighted PDW contrast MRI sequence was chosen in this study as it is frequently used to assess pathologies of the knee in a clinical setting 11 21. Creating an anteriorposterior view as if scrolling through the knee from front to back and vice versa.
Sagittal proton-density image of the knee showing an ovoid intermediate density lesion white arrow anterior to the reconstructed ACL. To compare the imaging appearance of knee abnormalities depicted with a 5-minute 3D double-echo in steady-state DESS sequence with separate echo images with that of a routine clinical knee MRI protocol. Assessment of anterior subcutaneous hypersignal on proton-density-weighted MR imaging of the knee and relationship with anterior knee pain.

Proton Density Weighted Fat Suppressed Mri Of The Knee Sequentially Download Scientific Diagram
Magnetic Resonance Images Of The Knee Joint Sagittal Proton Density Images In Cine Mode Mri Knee Joint Showing The Anatomy Of The Knee Stock Photo Alamy

Synthetic Mri Of The Knee Phantom Validation And Comparison With Conventional Mri Radiology

A Quality Audit Of Mri Knee Exams With The Implementation Of A Novel 2 Point Dixon Sequence Bastian Jordan 2019 Journal Of Medical Radiation Sciences Wiley Online Library
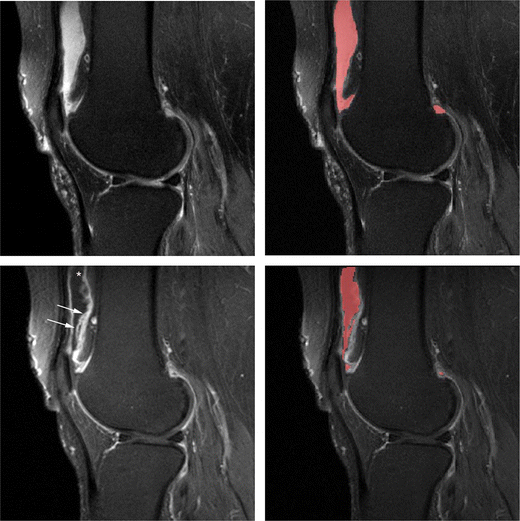
Mri Based Volumetric Assessment Of Joint Effusion In Knee Osteoarthritis Using Proton Density Weighted Fat Suppressed And T1 Weighted Contrast Enhanced Fat Suppressed Sequences Springerlink

In This Proton Density Sagittal Image No Anterior Cruciate Ligament Download Scientific Diagram
Mri Coronal T1 Sagittal Axial Proton Density With Fat Suppression Download Scientific Diagram
Mri Images Knee Mri Coronal Pd Spir 001 Mr Tip Com

Musculoskeletal Mri Body Mri Research Group Bmr Stanford Medicine
Assessment Of 3 T Mri Using Susceptibility Weighted Imaging To Detect And Evaluate Intra Or Periarticular Blood Metabolites And Meniscal Tears Of The Knee

Sagittal Proton Density Pd Weighted Mri Of A Non Operated Knee Download Scientific Diagram

Figure 1 Automated Segmentation Of Trabecular And Cortical Bone From Proton Density Weighted Mri Of The Knee Springerlink

A Coronal Proton Density B Coronal T2 Weighted Fat Suppressed Download Scientific Diagram

Sagittal Proton Density Weighted Mri Of The Knee Of A 21 Year Old Male Download Scientific Diagram

Post a Comment
Post a Comment